Note
This tutorial was generated from an IPython notebook that can be downloaded here.
Create xarray region mask¶
In this tutorial we will show how to create a mask for arbitrary latitude and longitude grids using xarray. It is very similar to the tutorial Create Mask (numpy).
Import regionmask and check the version:
import regionmask
regionmask.__version__
'0.9.0'
Load xarray and the tutorial data:
import xarray as xr
import numpy as np
airtemps = xr.tutorial.load_dataset('air_temperature')
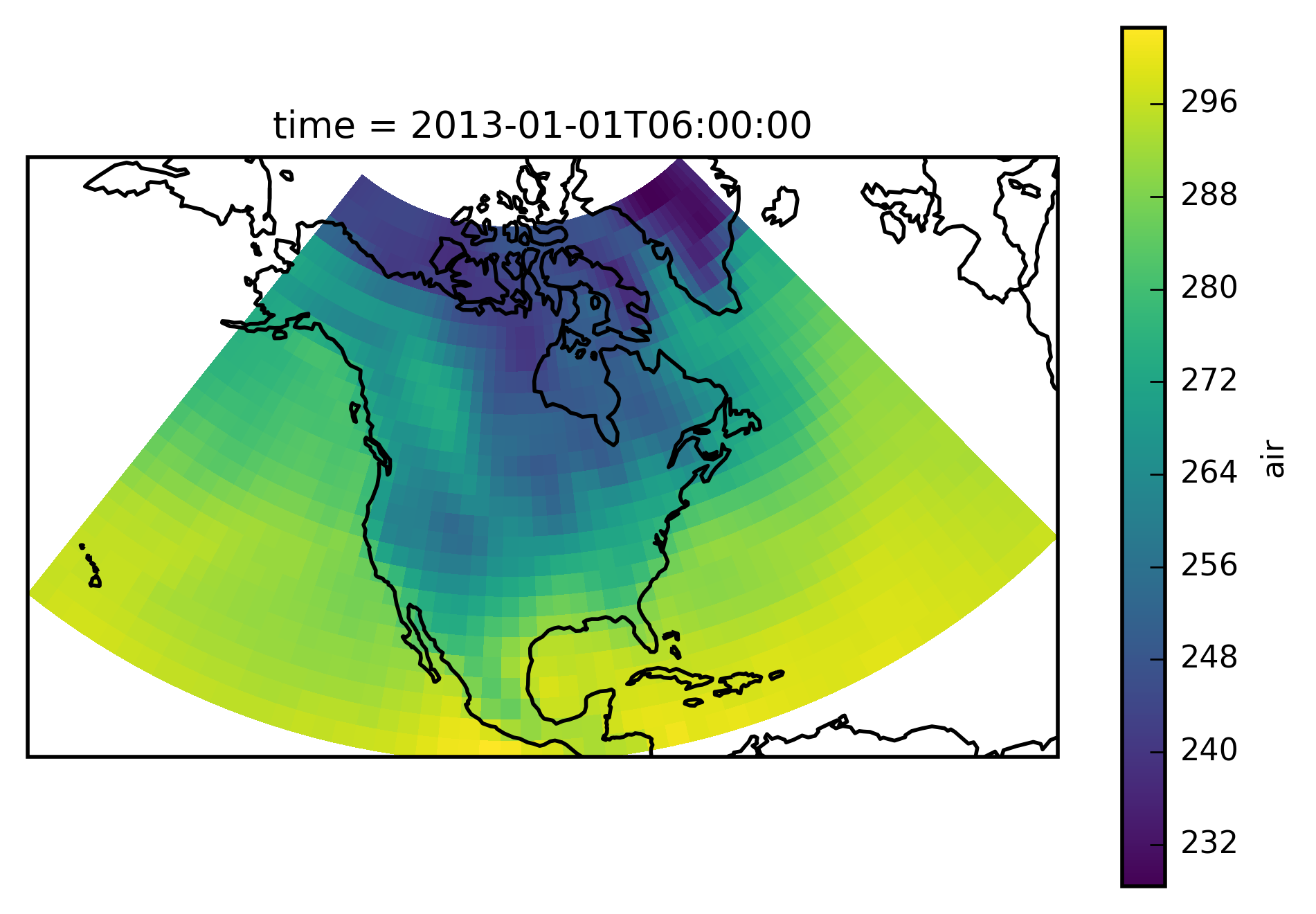
The example data is a temperature field over North America. Let’s plot the first time step:
# load cartopy
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
# choose a good projection for regional maps
proj=ccrs.LambertConformal(central_longitude=-100)
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection=proj)
airtemps.isel(time=1).air.plot.geocolormesh(ax=ax, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.coastlines();
/home/mathause/.local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/matplotlib/artist.py:221: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: This has been deprecated in mpl 1.5, please use the
axes property. A removal date has not been set.
warnings.warn(_get_axes_msg, mplDeprecation, stacklevel=1)
Conviniently we can directly pass an xarray object to the mask
function. It gets the longitude and latitude from the DataArray/ Dataset
and creates the mask. If the longituda and latitude in the xarray
object are not called lon and lat, respectively; their name can
be given via the lon_name and lat_name keyword. Here we use the
Giorgi regions.
mask = regionmask.giorgi.mask(airtemps)
print('All NaN? ',np.all(np.isnan(mask)))
All elements of mask are NaN. Try to set 'wrap_lon=True'.
All NaN? True
This didn’t work - all elements are NaNs! The reason is that airtemps
has its longitude from 0 to 360 while the Giorgi regions are defined as
-180 to 180. Thus we can provide the wrap_lon keyword:
mask = regionmask.giorgi.mask(airtemps, wrap_lon=True)
print('All NaN? ',np.all(np.isnan(mask)))
All NaN? False
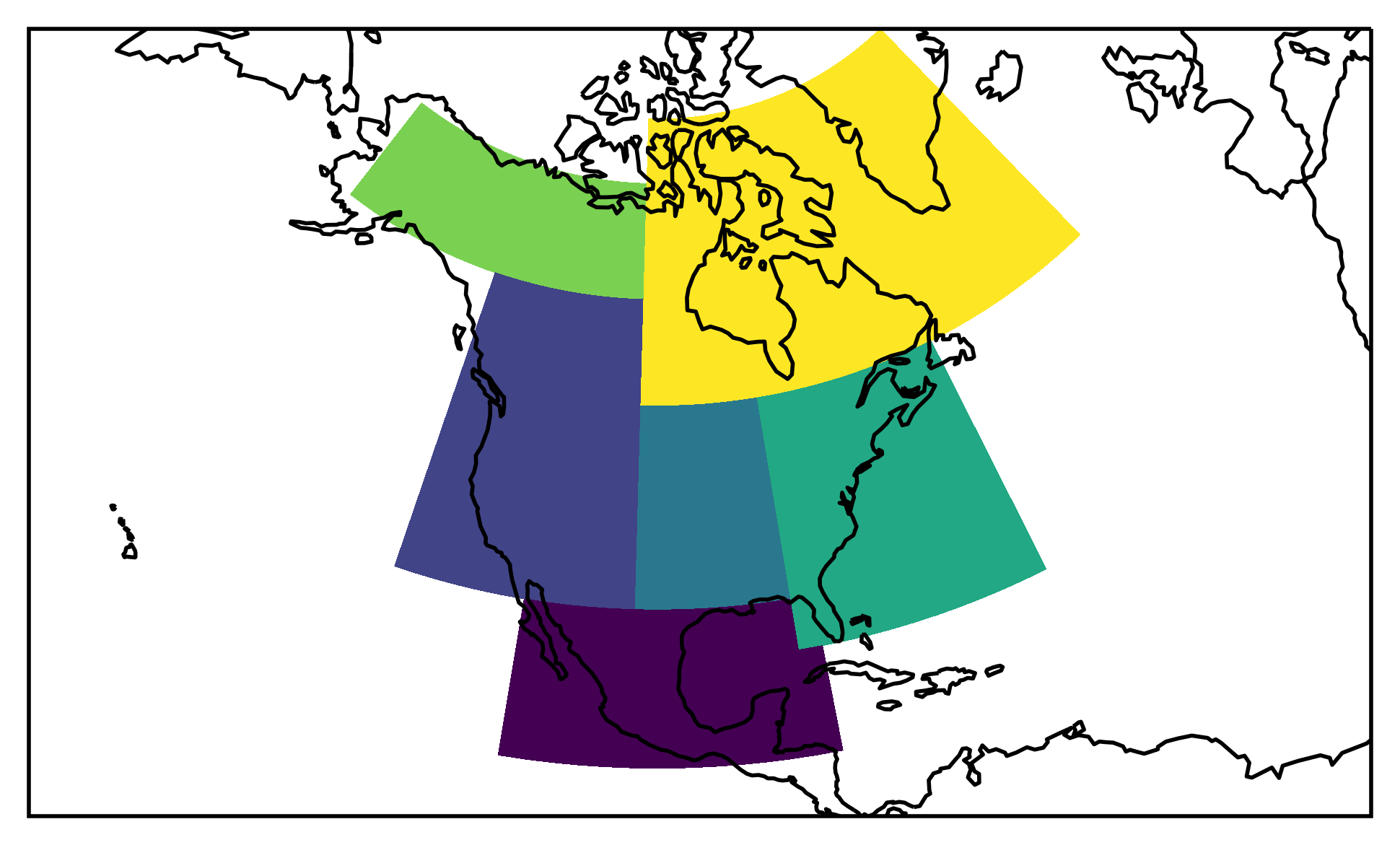
This is better. Let’s plot the regions:
proj=ccrs.LambertConformal(central_longitude=-100)
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection=proj)
low = mask.min()
high = mask.max()
levels = np.arange(low - 0.5, high + 1)
mask.plot.pcolormesh(ax=ax, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(), levels=levels, add_colorbar=False)
ax.coastlines()
# fine tune the extent
ax.set_extent([200, 330, 10, 75], crs=ccrs.PlateCarree());
We want to select the region ‘Central North America’. Thus we first need to find out which number this is:
regionmask.giorgi.map_keys('Central North America')
6
xarray provides the handy where function:
airtemps_CNA = airtemps.where(mask == 6)
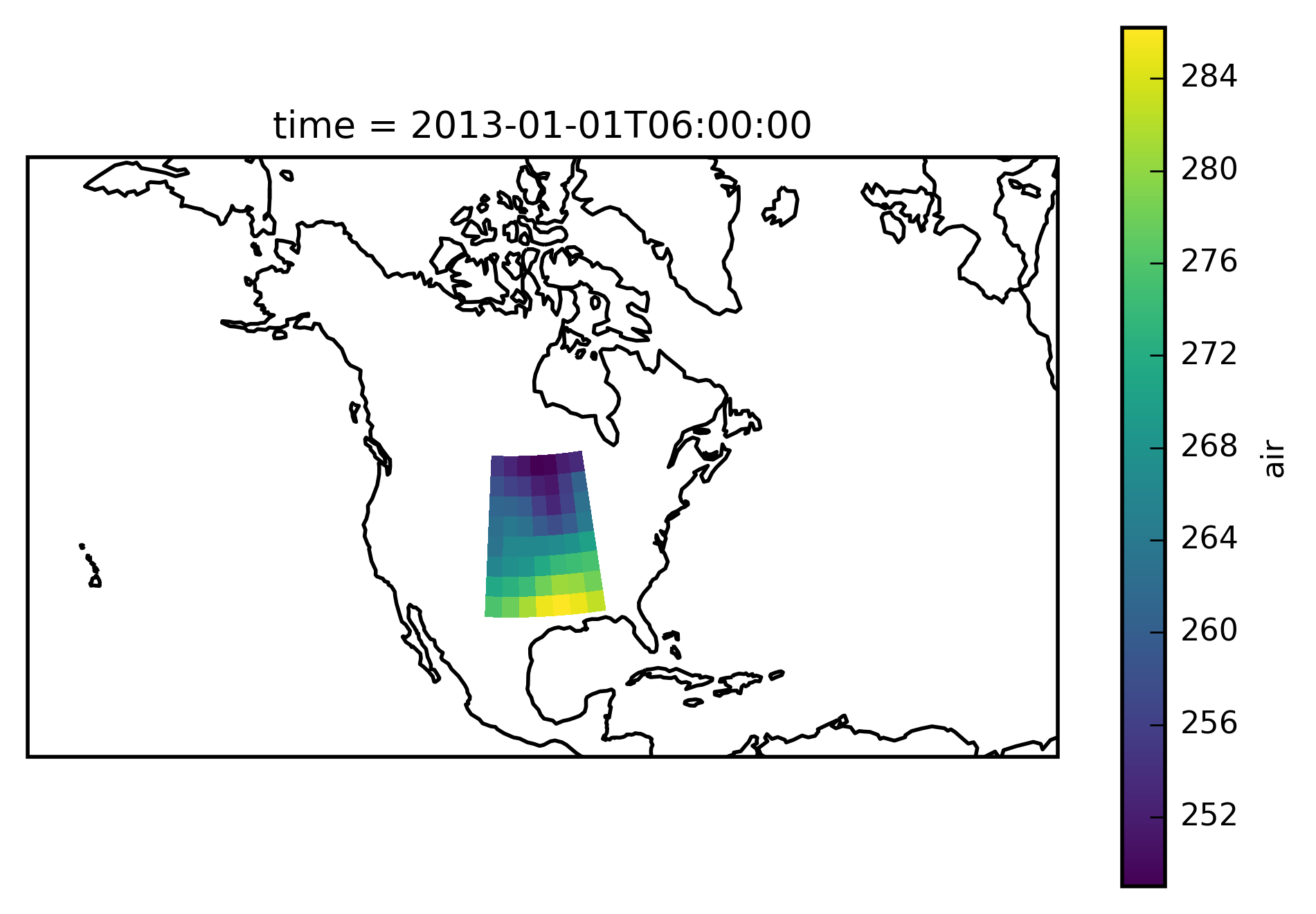
Check everything went well by repeating the first plot with the selected region:
# choose a good projection for regional maps
proj=ccrs.LambertConformal(central_longitude=-100)
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection=proj)
airtemps_CNA.isel(time=1).air.plot.geocolormesh(ax=ax, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.coastlines();
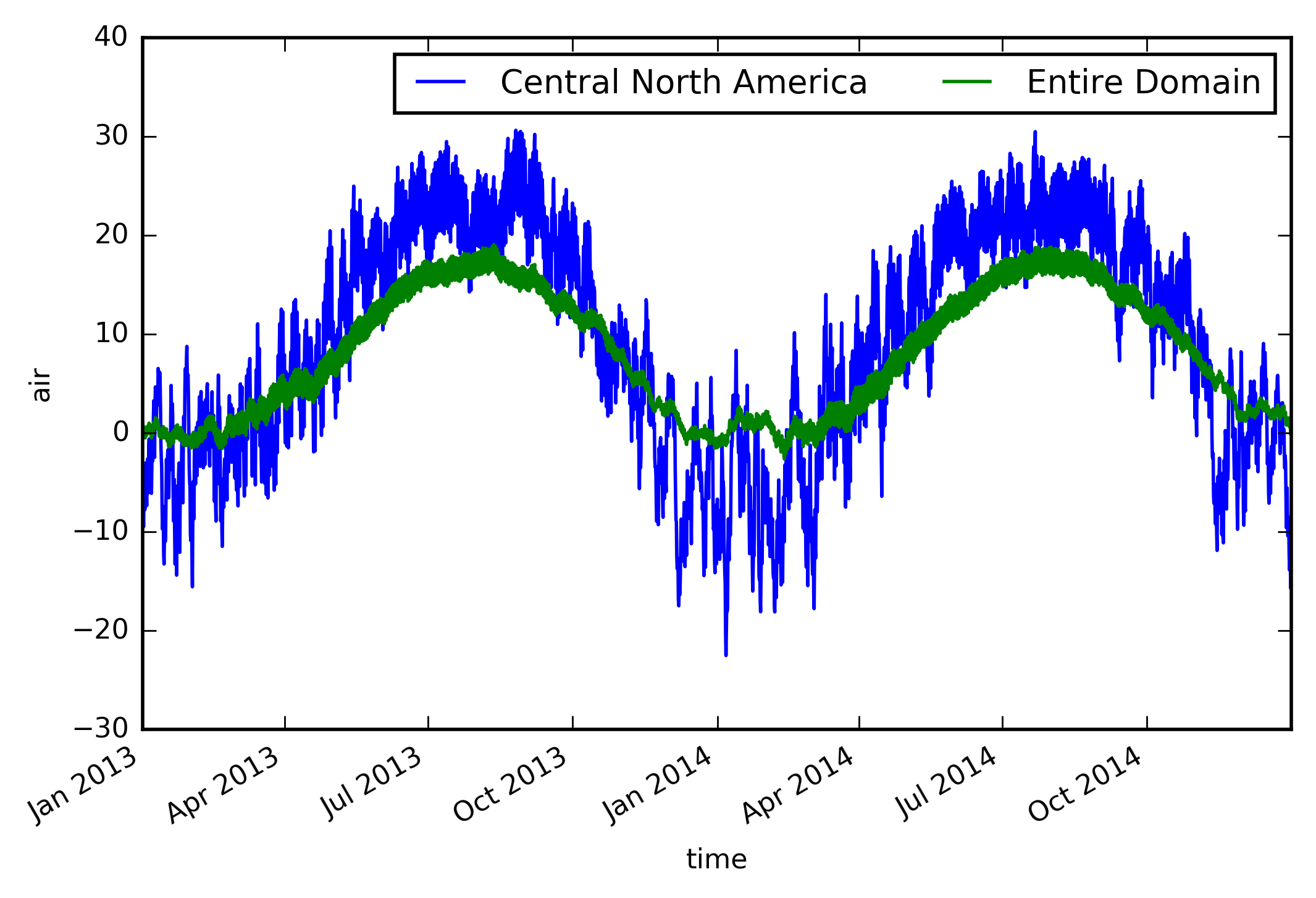
Looks good - let’s take the area average and plot the time series.
(Note: you should use cos(lat) weights to correctly calculate an
area average. Unfortunately this is not yet (as of version 0.7)
implemented in xarray.)
ts_airtemps_CNA = airtemps_CNA.mean(dim=('lat', 'lon')) - 273.15
ts_airtemps = airtemps.mean(dim=('lat', 'lon')) - 273.15
# and the line plot
ts_airtemps_CNA.air.plot.line(label='Central North America')
ts_airtemps.air.plot(label='Entire Domain')
plt.legend(ncol=2)
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x2adada801dd0>